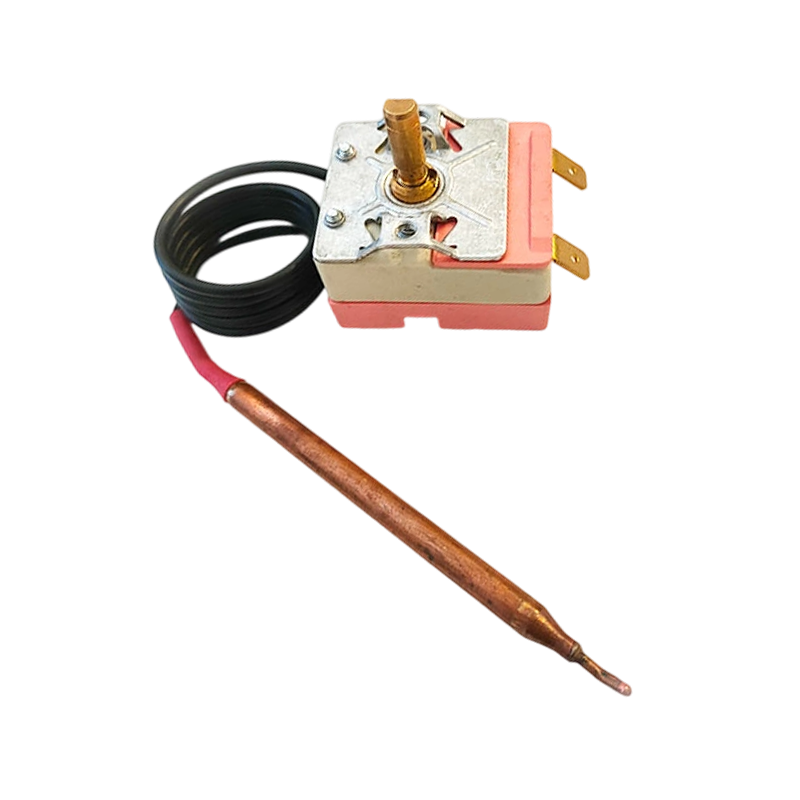
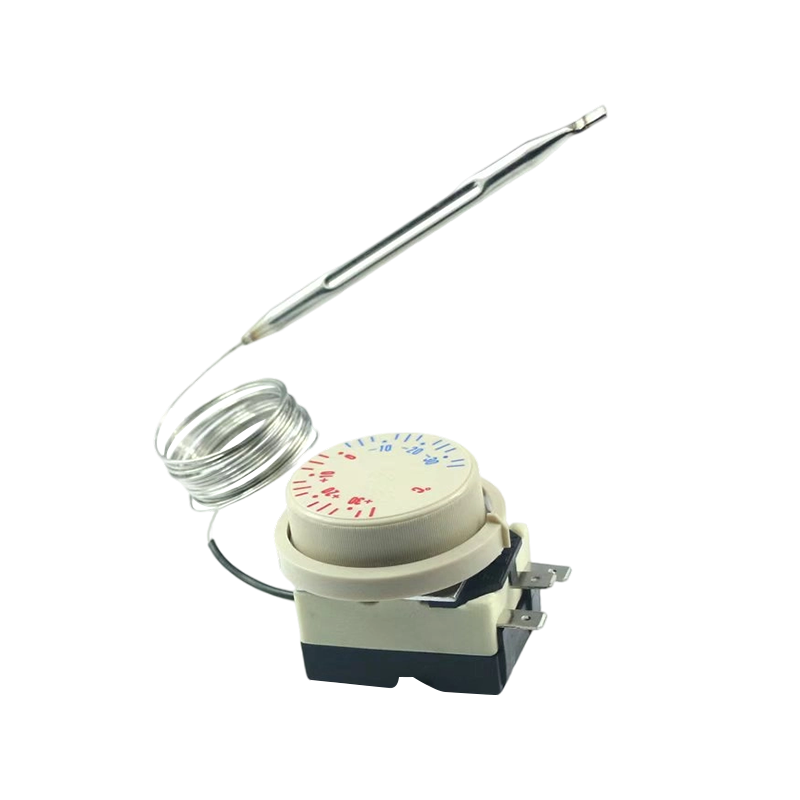
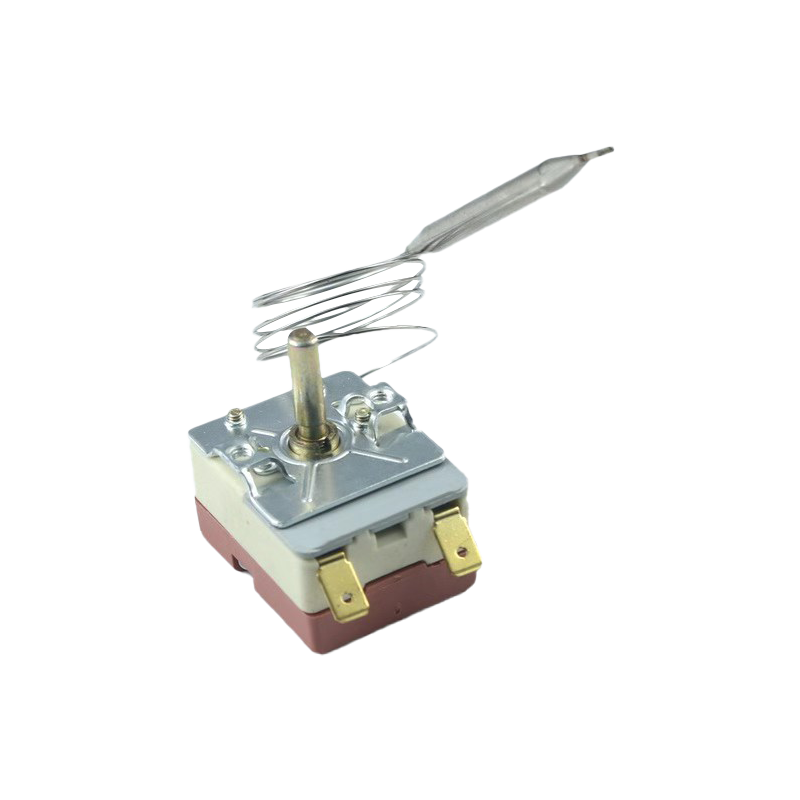
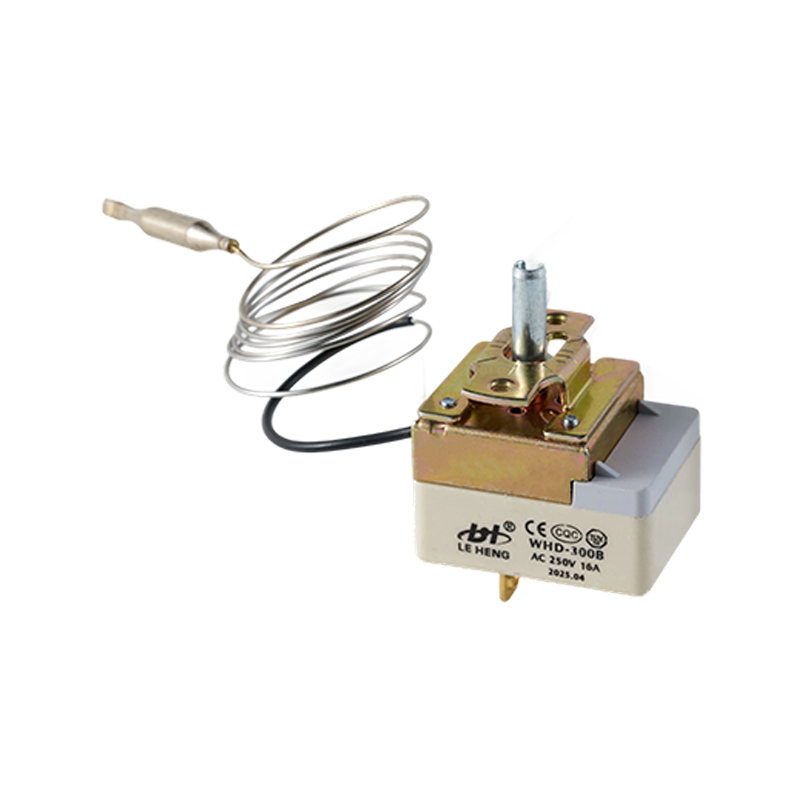
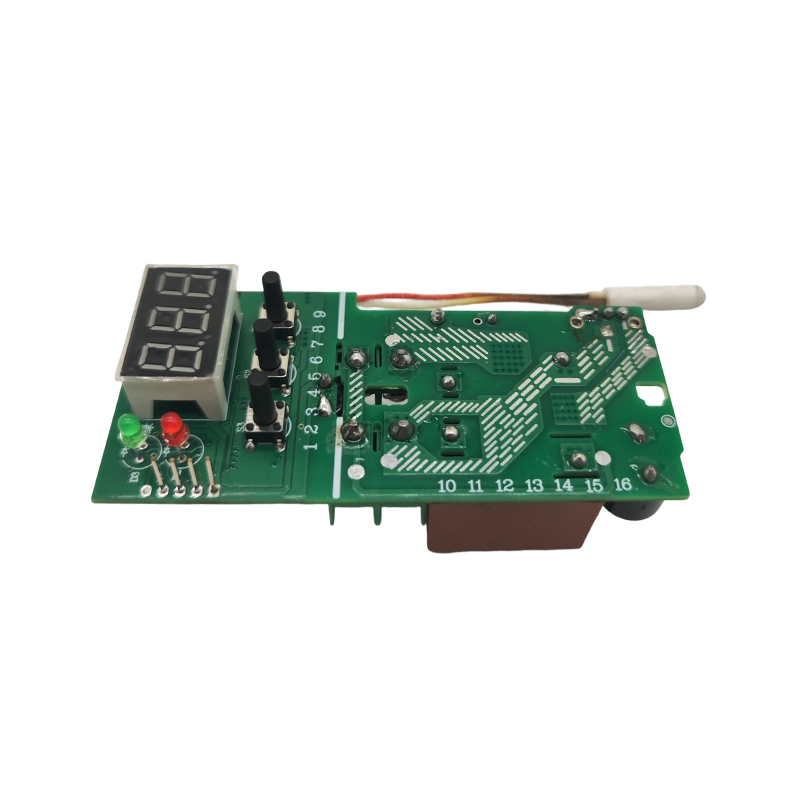
The WHD-711 adjustable thermostat is designed for cooling systems. It offers precise tempe...

-
Spring has arrived, and all things are flourishing. Our resumption of work conference concluded successfully amidst enthusiasm and focus, marking the official start of a new journey in 2026. Returning...
READ MORE -
A limit thermostat is a crucial safety component found inside furnace systems, designed to monitor internal heat levels and prevent overheating. Within a furnace, the limit thermostat helps maintain s...
READ MORE -
A limit thermostat and a normal thermostat are both temperature-related components found in heating systems, but their responsibilities are very different. The limit thermostat focuses on safety prote...
READ MORE -
A limit thermostat is often mentioned alongside standard temperature controllers, yet the two devices serve very different purposes within heating systems. The limit thermostat operates as a protectiv...
READ MORE -
A limit thermostat plays a critical role in heating systems by monitoring internal temperatures and acting as a safety control when abnormal heat conditions occur. Unlike comfort-focused temperature c...
READ MORE
Refrigeration thermoreats play a central role in temperature regulation across commercial, industrial, and domestic cooling systems. These thermoreatic devices monitor temperature conditions and activate or deactivate components such as compressors, evaporator fans, and defrost mechanisms to maintain stable operating ranges.
Overview of Refrigeration Thermoreat Technology
A refrigeration thermoreat is a temperature-dependent control device that responds to changes in the surrounding medium. When temperature shifts beyond the preset range, the thermoreat initiates an electrical switch action that regulates the refrigeration cycle.
Common refrigeration thermoreats can be classified based on:
Functional Operation
- On/Off Mechanical Control
Uses internal mechanical components such as bellows or capillary tubes to switch circuits.
- Electric or Electronic Control
Utilizes sensors, circuit boards, or digital interfaces for enhanced precision.
- Multistage Control
Offers multiple switching stages for systems requiring tiered cooling outputs.
Adjustment Method
- Fixed Temperature Type
Designed for applications requiring predetermined temperature limits.
- Adjustable Temperature Type
Allows users to set temperature ranges based on system requirements.
Structural Style
- Capillary-Type Thermoreat
Uses a fluid-filled capillary and sensing bulb.
- Mechanical Contact Thermoreat
Incorporates bimetal or bellows mechanisms.
- Electronic Thermoreat
Utilizes digital sensors and microcontrollers.
Adjustable Commercial Thermoreat
Definition and General Features
An Adjustable Commercial Thermoreat is a mechanical or electronic device used primarily in commercial refrigeration equipment. It permits temperature modification through a dial or digital interface, enabling operators to accommodate varying storage conditions. These thermoreats are built to withstand frequent cycling and environmental fluctuations encountered in commercial settings.
Functional Characteristics
Wide adjustable temperature span to accommodate diverse cooling applications.
Mechanical durability for repeated compressor control cycles.
Flexible sensing configurations, such as remote sensing bulbs or surface-mounted probes.
Compatibility with various refrigerants, depending on the design.
Common Applications
- Merchandising refrigerators
- Display freezers
- Food preparation counters
- Beverage chillers
- Commercial ice-making equipment
Advantages
Provides adaptable temperature management for changing product requirements.
Allows manual fine-tuning to match ambient variations.
Simple installation and maintenance procedures.
Adjustable Temperature Refrigeration Thermoreat
Definition
The Adjustable Temperature Refrigeration Thermoreat enables precise user-defined temperature settings for refrigeration systems. It typically includes a responsive sensing element—such as a bulb and capillary assembly—that detects temperature changes and adjusts system operations accordingly.
Structural Components
Typical components may include:
- Temperature sensing bulb
- Capillary tube
- Mechanical switch assembly
- Adjustable dial or interface
- Connection terminals
Functional Highlights
User-defined temperature setpoint, enabling flexibility for various cooling tasks.
High response sensitivity to temperature fluctuations.
Stable switching performance for compressor protection.
Optional features, such as defrost integration or dual-function switching.
Usage Scenarios
- Domestic refrigerators and freezers
- Commercial cooling cabinets
- Refrigerated transport units
- Refrigeration display cases
Cooling systems in laboratories or controlled environments
Classification of Refrigeration Thermoreats
Refrigeration thermoreats can be grouped in multiple ways based on sensing method, adjustment capability, and application requirements. Below is a detailed breakdown.
Classification by Sensing Mechanism
| Classification | Sensing Element | Typical Application | Key Feature |
| Capillary Refrigeration Thermoreat | Bulb + capillary with fluid | Refrigerators, freezers | Highly responsive mechanical sensing |
| Mechanical Contact Thermoreat | Bimetal or bellows | Simple cooling devices | Robust structure |
| Electronic Refrigeration Thermoreat | Digital sensor or probe | Precision refrigeration systems | Programmable control |
Classification by Application Environment
- Domestic Refrigeration Thermoreat
Used in household refrigerators and freezers.
Features simple structure, moderate switching capacity, and adjustable temperature ranges suitable for small cooling systems.
- Commercial Refrigeration Thermoreat
Designed for larger systems that run for extended periods.
Provides enhanced durability, adjustable temperature ranges, and compatibility with various types of refrigerants.
- Industrial Refrigeration Thermoreat
Applied in industrial cold rooms, production storage spaces, and process control cooling.
Often includes specialized sensory accuracy and multi-stage switching capabilities.
Classification by Adjustment Method
- Fixed Temperature Thermoreat
Used in systems requiring predetermined operation without user modification.
Common in compact appliances or simplified cooling units.
- Adjustable Temperature Thermoreat
Allows manual tuning of temperature ranges.
Essential for commercial refrigeration where product types or ambient conditions vary.
Key Performance Parameters and Technical Considerations
When evaluating Adjustable Commercial Thermoreats or Adjustable Temperature Refrigeration Thermoreats, several performance factors influence system compatibility and long-term reliability.
Temperature Range
Different refrigeration applications require specific operational ranges. Thermoreats should match the temperature needed for the particular cooling process.
Differential Control
The differential refers to the difference between cut-in and cut-out temperatures.
A suitable differential ensures energy-efficient cycling and avoids compressor strain.
Capillary Length and Bulb Size
Capillary dimensions must correspond to equipment layout. The sensing bulb size affects sensitivity and response time.
Switching Capacity
Higher-capacity switches are necessary for compressors with larger electrical loads or frequent on/off cycles.
Environmental Durability
Thermoreats may be exposed to moisture, vibration, hydrocarbons, or varying ambient temperatures, necessitating robust materials.
Installation Configuration
Common installation types include:
- Panel mounting
- Surface mounting
- Remote sensing installations
Comparison Between Adjustable Commercial and Adjustable Temperature Refrigeration Thermoreats
| Feature | Adjustable Commercial Thermoreat | Adjustable Temperature Refrigeration Thermoreat |
| Primary Use | Commercial cooling systems | Household and commercial refrigeration |
| Adjustment | Broad range for varied products | User-adjustable for precision cooling |
| Durability | High cycling endurance | Suitable for both light and moderate duty |
| Common Controls | Dial or knob adjustment | Dial or digital interface |
| Typical Installations | Display units, storage coolers | Refrigerators, chillers, display cabinets |
Applications Across Refrigeration Fields
Refrigeration thermoreats can be found in a wide assortment of equipment categories:
- Cold storage and cold rooms
- Supermarket refrigeration units
- Restaurant cooling appliances
- Medical and laboratory refrigeration
- Refrigerated transportation
- Ice cream cabinets and merchandising freezers
- Food processing and preservation equipment
Each application may require different thermoreat specifications depending on cooling load, environmental exposure, and control precision.
Future Trends in Refrigeration Thermoreat Development
As cooling technologies evolve, thermoreat design is also progressing. The following trends are shaping the industry:
- Integration With Digital Monitoring
Smart sensors and digital interfaces are increasingly used to provide real-time temperature feedback and system diagnostics.
- Improved Energy Efficiency
Thermoreats are being engineered to reduce unnecessary compressor cycling and promote balanced system operation.
- Adaptation to New Refrigerants
Modern cooling systems may require thermoreats compatible with alternative refrigerants that meet updated environmental standards.
- Enhanced Safety and Reliability
Thermoreats are being equipped with improved materials and safety cutoff designs to protect compressors and maintain stable operation.
Refrigeration thermoreats—especially the Adjustable Commercial Thermoreat and the Adjustable Temperature Refrigeration Thermoreat—remain essential components in maintaining consistent and efficient cooling performance across a wide range of applications. These thermoreat types contribute to stable temperature regulation, safe system operation, and flexible environmental management, making them integral to modern refrigeration technology.



 English
English Türk
Türk