WHD-E copper adjustable copper capillary thermostat is a mechanical temperature regulating devic...
Capillary Thermostat China: Production Features and Material Selection Guide
Understanding Manufacture and Composition
The consistent performance of a capillary thermostat is a direct result of specific manufacturing processes and deliberate material choices. The production landscape for capillary thermostat China combines methodical assembly techniques with a strategic approach to sourcing and utilising materials. This guide examines the typical production flow and provides insights into how material selection influences the final product's characteristics, offering clarity for those specifying or sourcing these components.
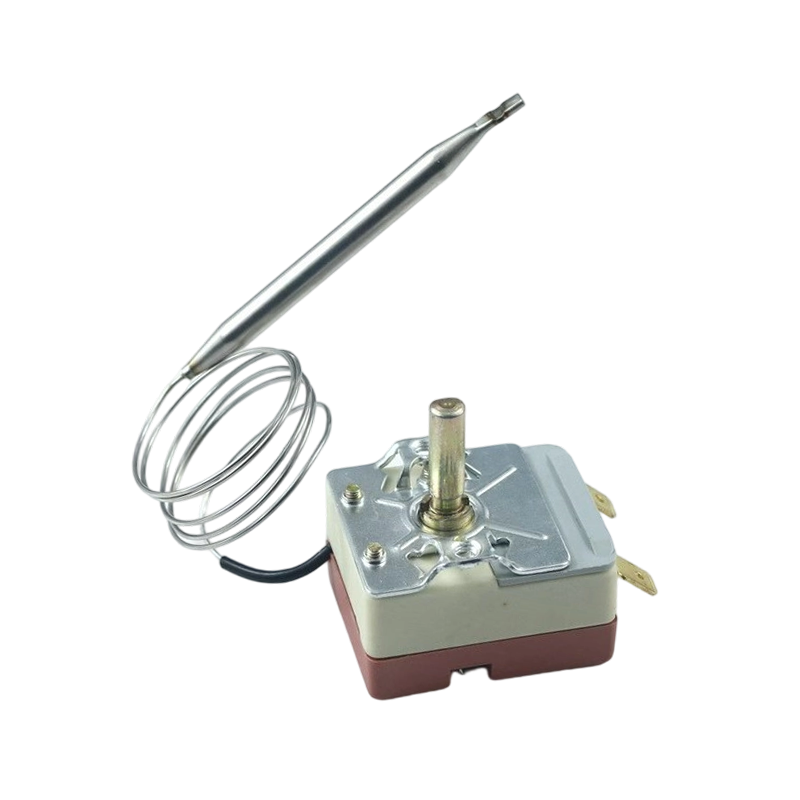

Typical Production Process and Core Techniques
Manufacturing a capillary thermostat involves a sequence of specialised steps designed to ensure accuracy and reliability. The process typically begins with the fabrication and preparation of key metal parts, such as the capillary tube, bulb, and switch housing. A central and delicate phase is the charging operation, where a precise amount of thermal expansion fluid is introduced into the sealed capillary system under controlled conditions. This step is fundamental to achieving the desired temperature response.
Following this, calibration is performed. Devices are subjected to known temperatures, and the switching mechanism is adjusted to activate at the specified set point. Many facilities employ automated calibration stations to enhance consistency across large production batches. Finally, each unit undergoes functional testing. This often includes electrical tests to verify switching action, insulation, and sometimes life cycle testing on a sample basis to validate durability.
Critical Components and Material Choices
The selection of materials for each component is a balancing act between performance, environment, and economic factors. The capillary tube and sensing bulb, which directly interact with the controlled environment, are commonly made from copper for its thermal conductivity and malleability. For applications involving corrosion risks, such as exposure to certain chemicals or moisture, stainless steel tubes may be selected.
The electrical contacts within the switch mechanism are another focal point. Materials like silver alloys are frequently used due to their strong electrical conductivity. The specific formulation can be chosen to manage factors like arc resistance when switching inductive loads. The external housing and internal insulating parts are often moulded from engineering plastics, such as PBT or phenolic resin, chosen for their electrical insulation properties, heat resistance, and dimensional stability. The choice of sensing fluid itself, whether a gas or liquid, defines the thermostat's operational temperature range and sensitivity.
A Framework for Informed Material Decisions
Navigating material options requires aligning component properties with application demands. For a standard residential appliance operating in a benign environment, a copper tube and standard contact material may provide a functional and economical solution. In contrast, a thermostat intended for an industrial setting with high humidity, chemical exposure, or significant vibration might necessitate stainless steel construction, specialised contacts, and a housing material with enhanced chemical resistance.
Engaging in a dialogue about materials with a manufacturer is beneficial. Describing the application's environmental stressors—such as constant moisture, potential for physical impact, or exposure to oils—allows the manufacturer to suggest a material set that can maintain performance over the device's expected lifespan. This collaborative approach helps in specifying a component that is fit for its purpose without unnecessary specification.
The Interplay of Process and Substance
The journey from raw materials to a finished capillary thermostat involves careful process control and thoughtful material science. The production features found in the capillary thermostat China sector reflect an integration of these elements. By understanding how manufacturing steps like charging and calibration affect performance, and how material choices for the tube, contacts, and housing influence durability and suitability, buyers and designers can make more informed decisions, advanced to the successful integration of these essential control devices.
-
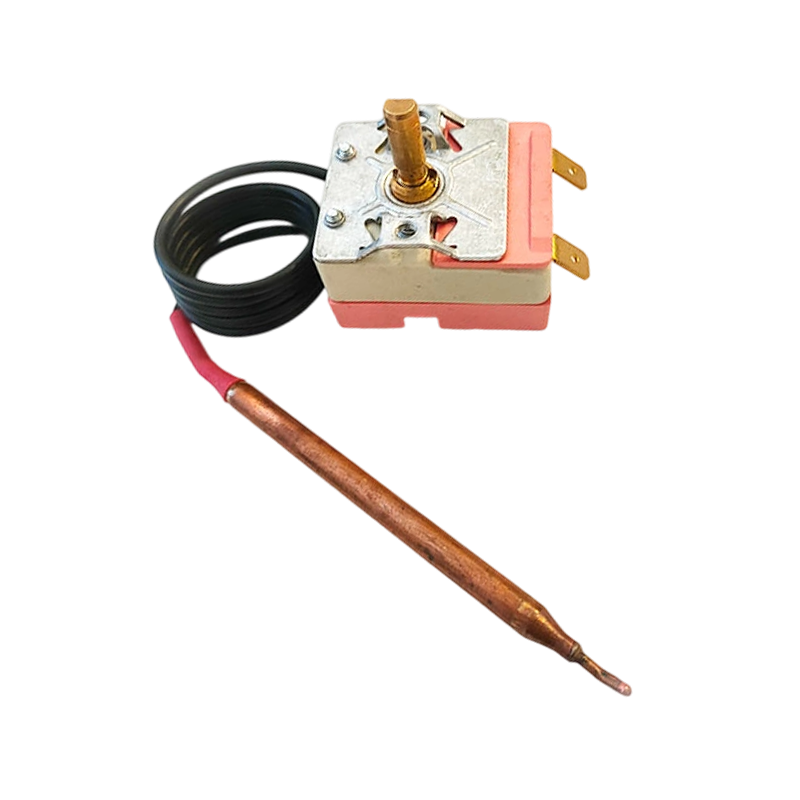

 WHD-E-CU Copper Adjustable Capillary Temperature Controller
WHD-E-CU Copper Adjustable Capillary Temperature Controller -
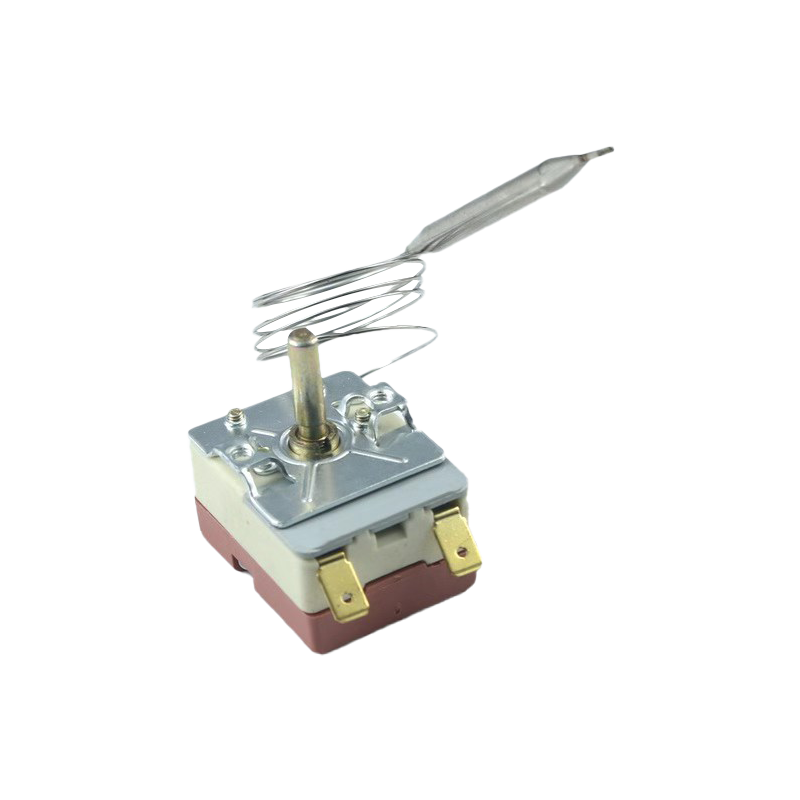
 Stainless Steel Adjustable Capillary Temperature Controller
Stainless Steel Adjustable Capillary Temperature ControllerThe stainless steel adjustable capillary thermostat is a mechanical temperature regulating devic...
-
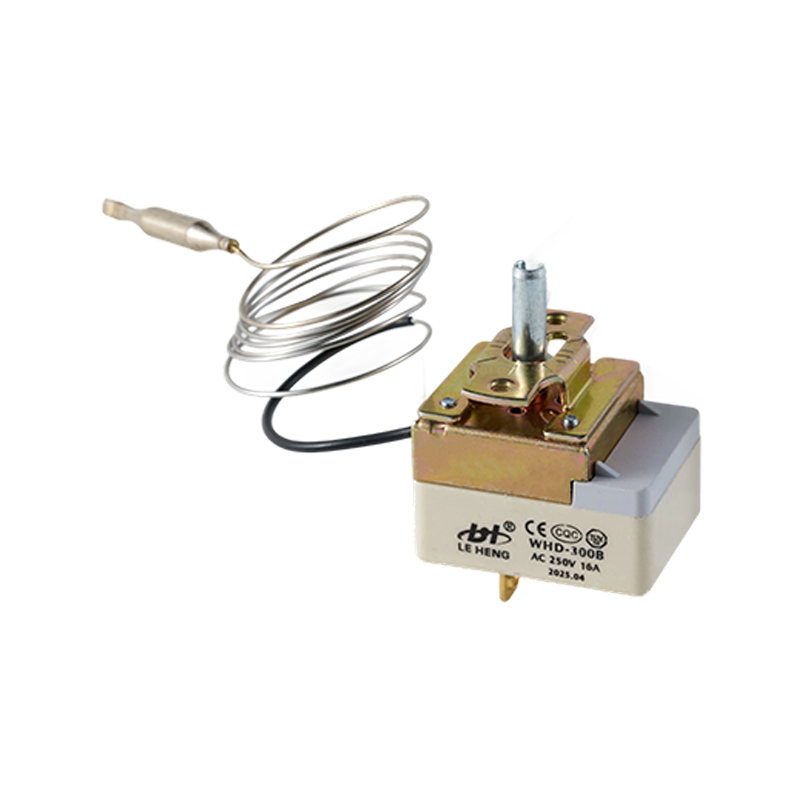
 WHD-B(16A/25A) Adjustable Temperature Mechanical Capillary Thermostat
WHD-B(16A/25A) Adjustable Temperature Mechanical Capillary ThermostatWHD-B(16A/25A) Adjustable Temperature Mechanical Capillary Thermostat is specially designed for ...
-
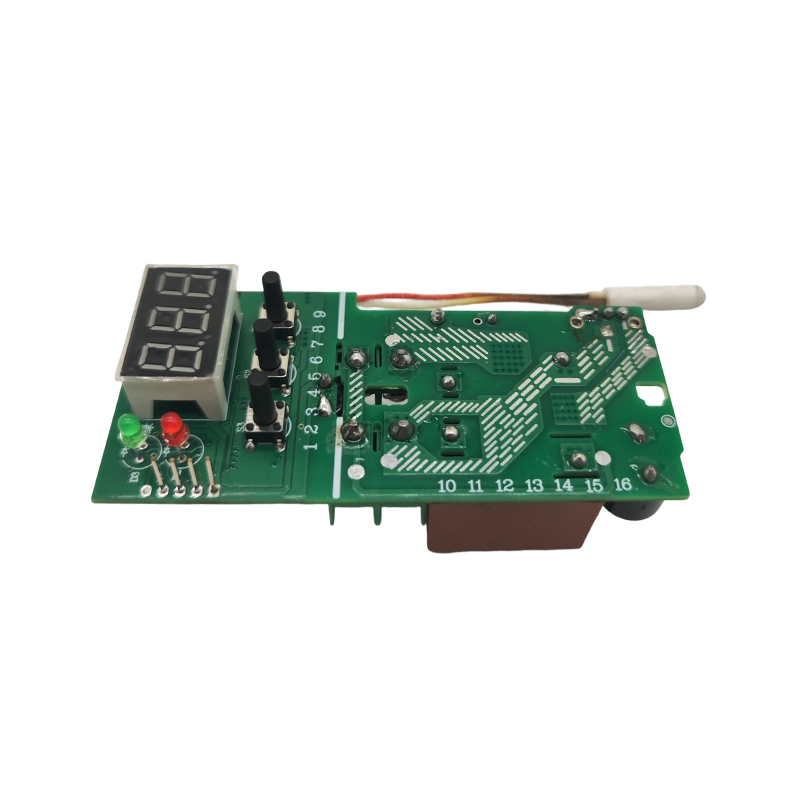
 WHD-RQ400-BY Digital Display Thermostatic Controller
WHD-RQ400-BY Digital Display Thermostatic ControllerThe WHD-RQ400-BY digital thermostat is an intelligent control device designed specifically for h...
-
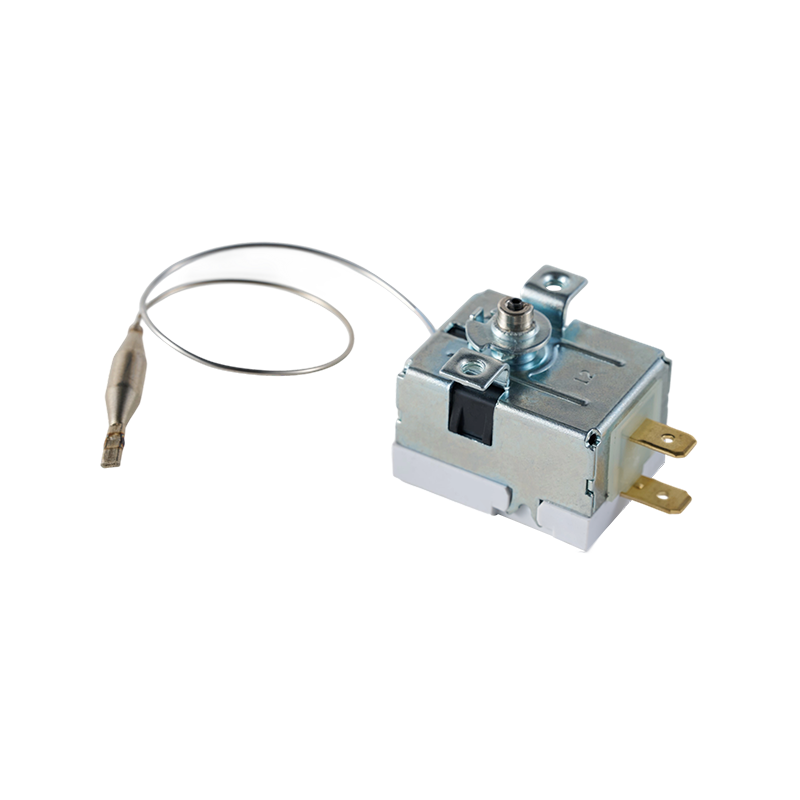
 WHD-H2 320 Degree Oven Heating Temperature Limiter
WHD-H2 320 Degree Oven Heating Temperature LimiterThe WHD-H2 oven heating limiter is designed for precise temperature control, with a maximum limi...
-
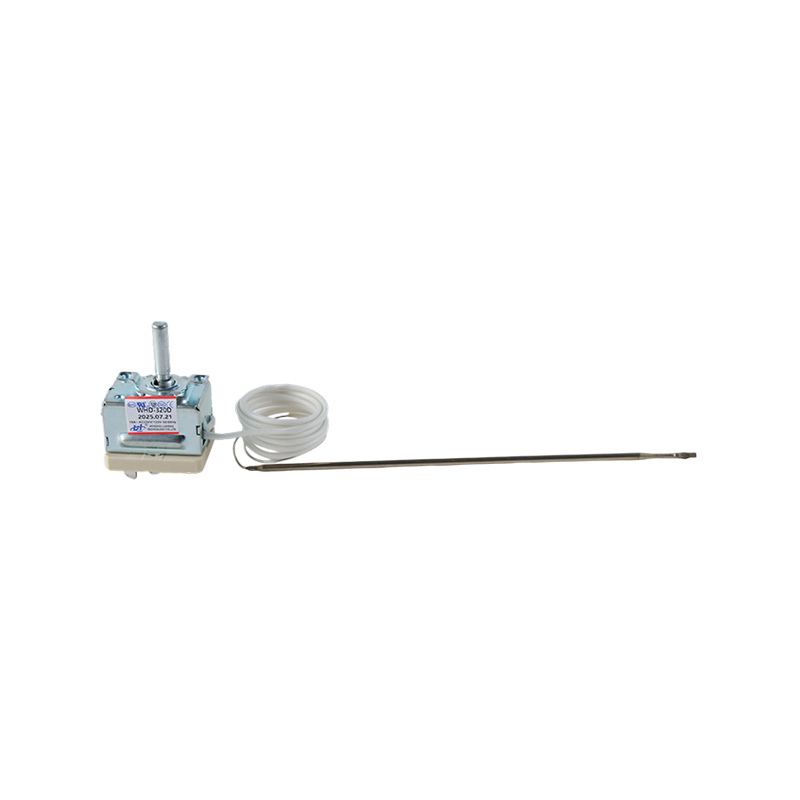

 WHD-D Adjustable Mechanical Temperature Thermostat
WHD-D Adjustable Mechanical Temperature ThermostatThe WHD-D adjustable mechanical thermostat offers reliable temperature control. It features a ma...
-

 WHD-YL260 Oil Furnace Digital Thermostat
WHD-YL260 Oil Furnace Digital ThermostatThe WHD-YL260 oil furnace thermostat is an intelligent temperature control device designed speci...
-
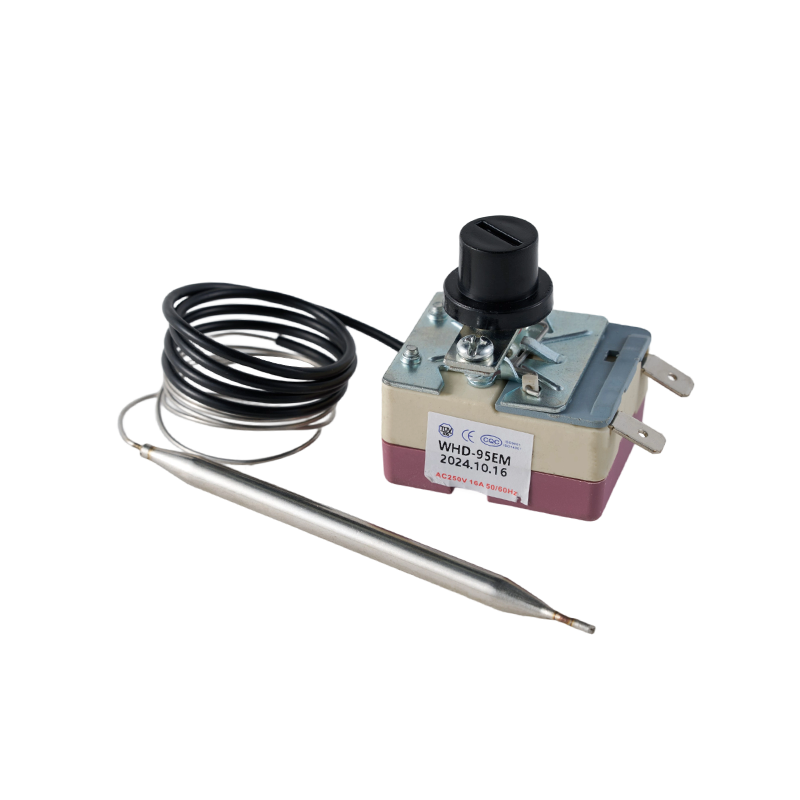

 WHD-EM Limit Temperature Controller
WHD-EM Limit Temperature ControllerThe WHD-EM limit temperature controller is a highly reliable device for critical temperature mon...
-
+86-15957748531
+86-15558959105
+86-18583671075
+86-18815077137 -
jilly@wzleh.com
east@wzleh.com
scott@wzleh.com
alan@wzleh.com
- STI Park #B-2, Hongqiao Yueqing City, Zhejiang, China, 325608




 English
English Türk
Türk
