WHD-E copper adjustable copper capillary thermostat is a mechanical temperature regulating devic...
Capillary Thermostat China: Precision Temperature Control for Refrigeration & Heating
Essential Control in Thermal Systems
In the fundamental cycles of removing or adding heat, precise temperature management is a cornerstone of efficiency and function. Capillary thermostat China serves as a key control point in these systems. The manufacturing sector focused on a capillary thermostat. China supplies a substantial volume of these components for both refrigeration and heating applications worldwide. This article examines their distinct roles in these two fields and the considerations for their effective use.

Role in Refrigeration Systems
Within refrigerators, freezers, and commercial cooling units, capillary thermostats perform several important functions. Their primary role is maintaining the cabinet interior within a defined temperature band, cycling the compressor on and off as needed. They are also integral to automatic defrost systems in frost-free appliances, activating heaters at set intervals to melt accumulated frost before returning to temperature control duty.
The operating environment here presents specific considerations. The thermostat must function reliably at lower temperatures, and its sensing element is often located in a cold, potentially humid space. Designs, therefore, account for factors like preventing condensation from affecting electrical parts. The reliability of the switching mechanism over thousands of cycles is important due to the compressor's frequent starting and stopping.
Function in Heating Applications
In electric heating devices, such as storage water heaters, space heaters, and various appliance warmers, capillary thermostats provide both control and protection. They regulate the heating element to maintain a consistent output temperature, such as keeping stored water at a preset level. A critical safety function is overtemperature protection, where the thermostat acts as a limit switch to cut power if normal control fails, helping to prevent hazardous conditions.
Heating applications introduce a different set of operational stresses. The thermostat, particularly its sensing bulb, is exposed to high temperatures. The electrical contacts may switch h higher inrush currents associated with heating elements. Construction materials must therefore maintain their insulating properties and mechanical strength at elevated temperatures, and contacts must be suited to the electrical load to ensure a long service life.
Guidance for Selection and Implementation
Choosing the right thermostat for a refrigeration or heating application involves focusing on parameters suited to each domain. For refrigeration, key selections include a temperature range that spans the desired control point and expected ambient conditions, a sensing bulb suitable for cold environments, and a design that manages moisture. For heating, the temperature rating must comfortably exceed the normal operating point, materials must withstand heat exposure, and electrical ratings must match the power load of the heater.
Proper installation influences performance. In refrigeration, ensuring the sensing bulb has solid thermal contact with the surface it is monitoring (like an evaporator coil) improves control accuracy. In heating applications, the correct placement of the sensing bulb in the water stream or air flow is important for a representative temperature reading. Understanding the difference between the control thermostat and the separate, often non-resettable, safety limit thermostat is also important in heater design.
Enabling Core Functionality
From preserving food to providing warm water, capillary thermostats are embedded in the functionality of essential everyday equipment. The focus on the capillary thermostat in China for these components highlights their role in global manufacturing. By appreciating the distinct requirements of refrigeration and heating systems—from environmental exposure to electrical loads—designers and engineers can specify and apply these thermostats in a way that supports the safe, efficient, and durable operation of the final product.
-
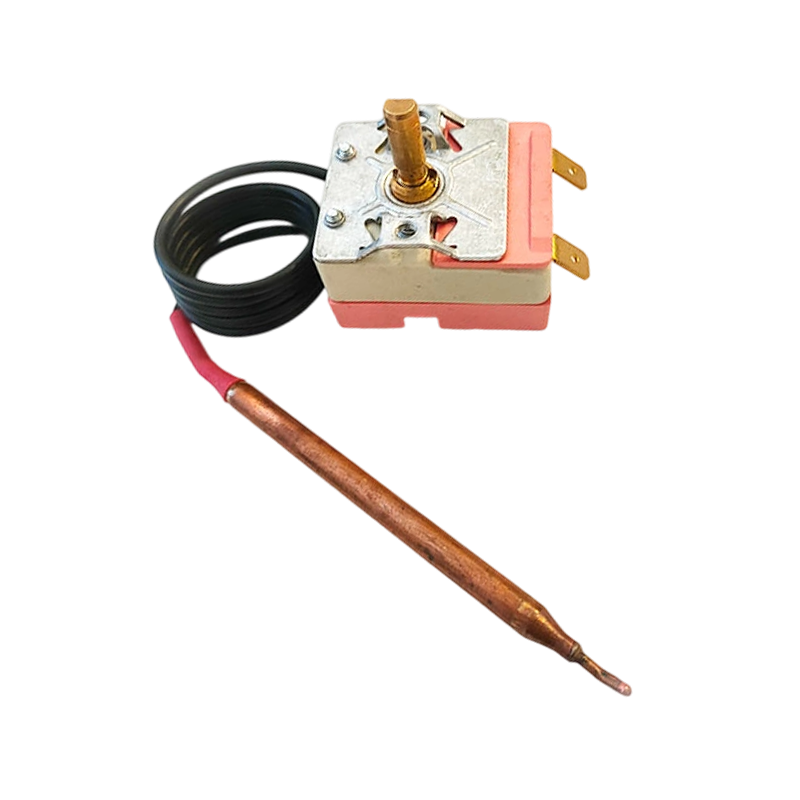

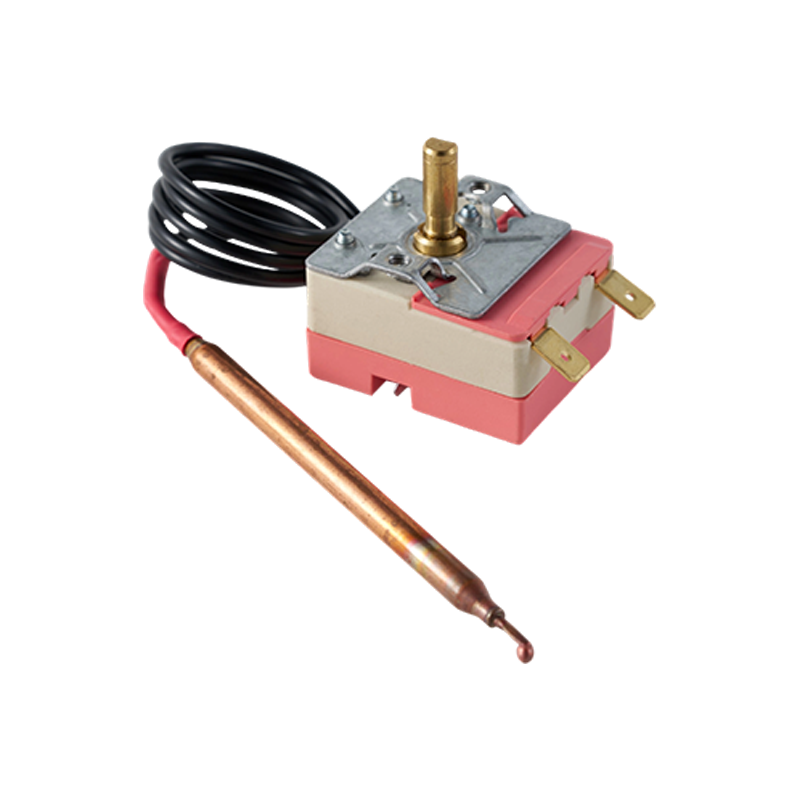
 WHD-E-CU Copper Adjustable Capillary Temperature Controller
WHD-E-CU Copper Adjustable Capillary Temperature Controller -
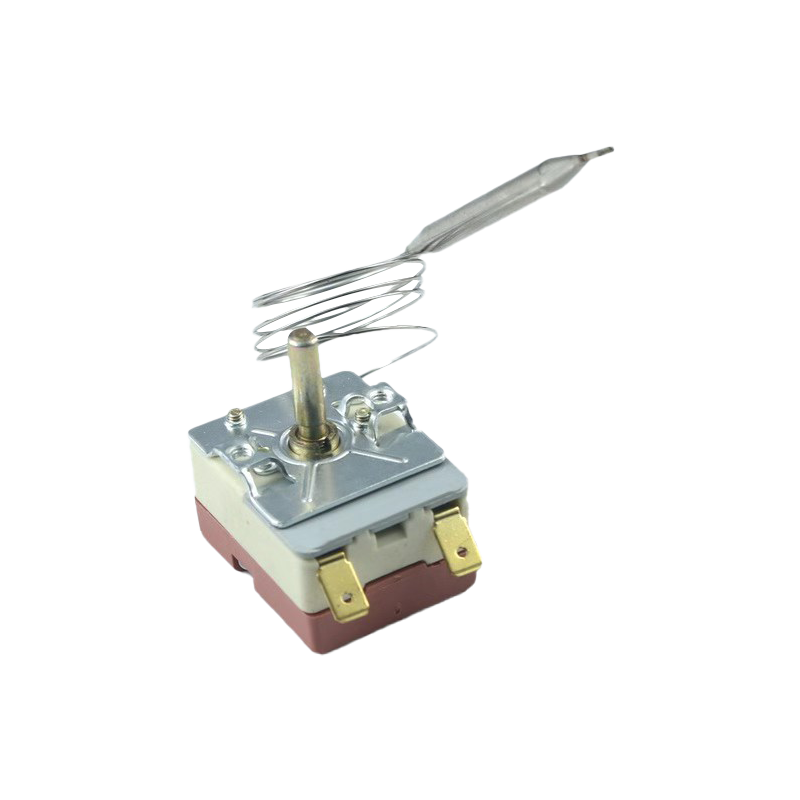
 Stainless Steel Adjustable Capillary Temperature Controller
Stainless Steel Adjustable Capillary Temperature ControllerThe stainless steel adjustable capillary thermostat is a mechanical temperature regulating devic...
-
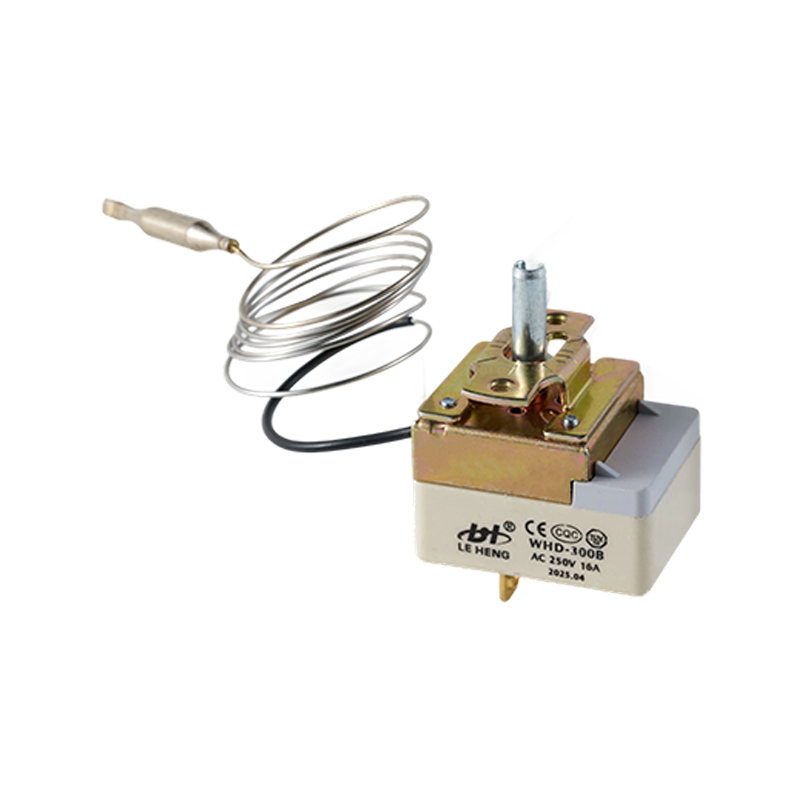
 WHD-B(16A/25A) Adjustable Temperature Mechanical Capillary Thermostat
WHD-B(16A/25A) Adjustable Temperature Mechanical Capillary ThermostatWHD-B(16A/25A) Adjustable Temperature Mechanical Capillary Thermostat is specially designed for ...
-
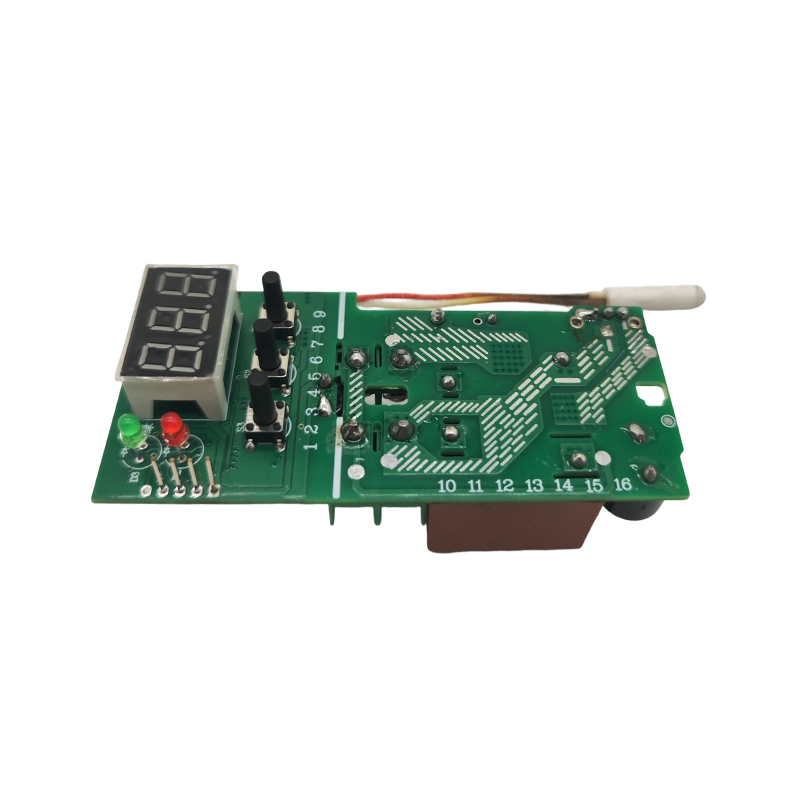
 WHD-RQ400-BY Digital Display Thermostatic Controller
WHD-RQ400-BY Digital Display Thermostatic ControllerThe WHD-RQ400-BY digital thermostat is an intelligent control device designed specifically for h...
-
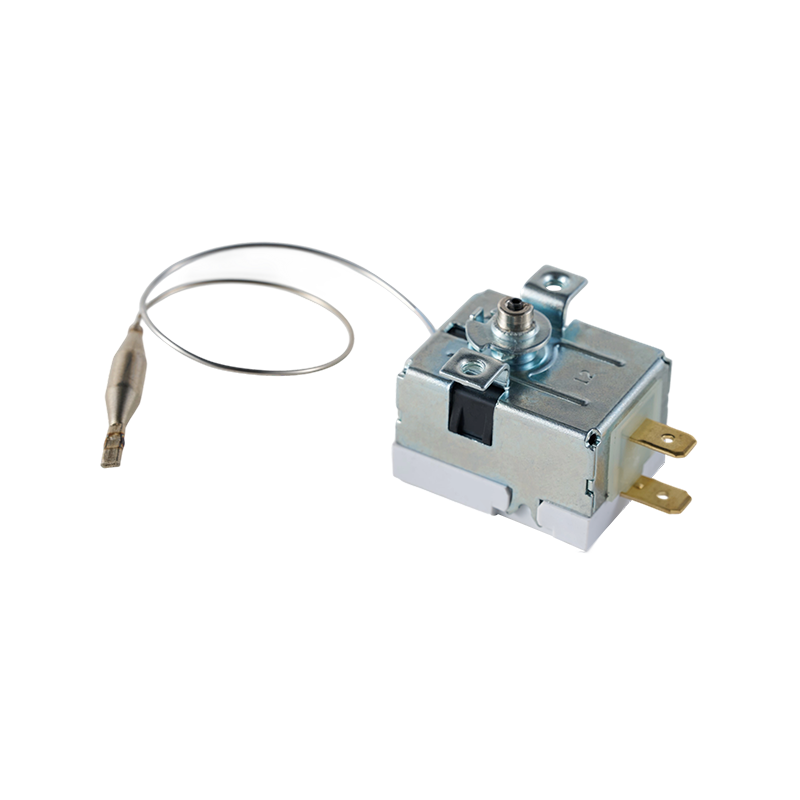
 WHD-H2 320 Degree Oven Heating Temperature Limiter
WHD-H2 320 Degree Oven Heating Temperature LimiterThe WHD-H2 oven heating limiter is designed for precise temperature control, with a maximum limi...
-
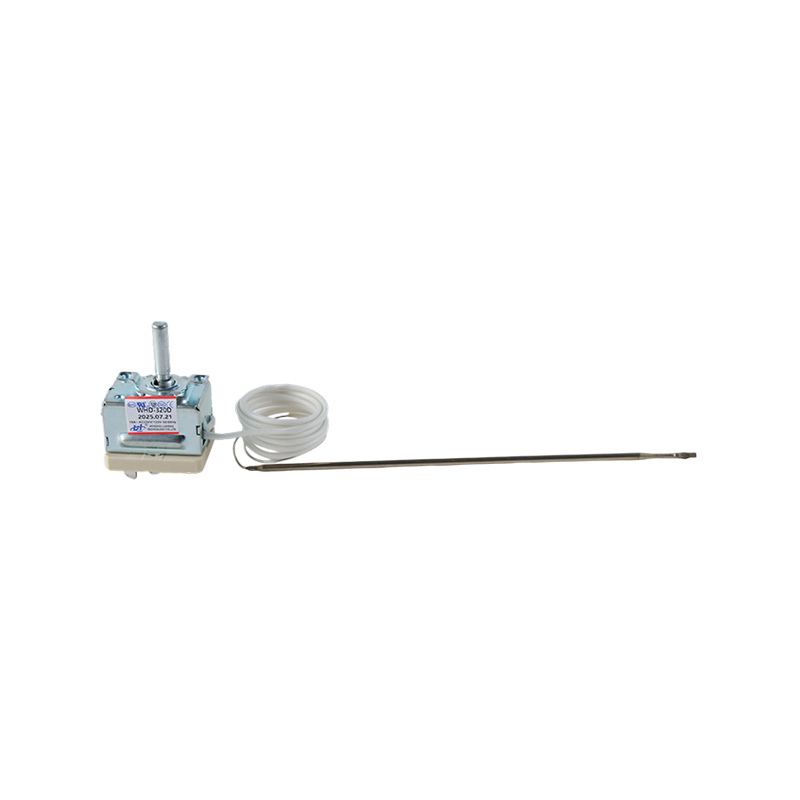

 WHD-D Adjustable Mechanical Temperature Thermostat
WHD-D Adjustable Mechanical Temperature ThermostatThe WHD-D adjustable mechanical thermostat offers reliable temperature control. It features a ma...
-

 WHD-YL260 Oil Furnace Digital Thermostat
WHD-YL260 Oil Furnace Digital ThermostatThe WHD-YL260 oil furnace thermostat is an intelligent temperature control device designed speci...
-
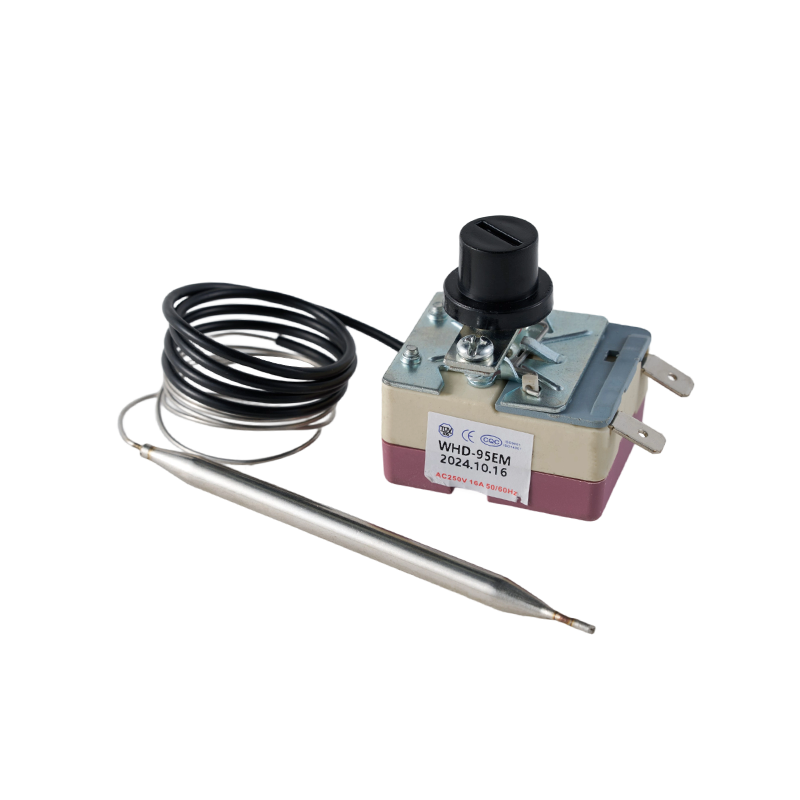

 WHD-EM Limit Temperature Controller
WHD-EM Limit Temperature ControllerThe WHD-EM limit temperature controller is a highly reliable device for critical temperature mon...
-
+86-15957748531
+86-15558959105
+86-18583671075
+86-18815077137 -
jilly@wzleh.com
east@wzleh.com
scott@wzleh.com
alan@wzleh.com
- STI Park #B-2, Hongqiao Yueqing City, Zhejiang, China, 325608




 English
English Türk
Türk
